Femmes et sciences : Université de Tel Aviv, le Pr Yael Hanein et son équipe développent une rétine artificielle
[:fr]Une équipe dirigée par le Prof. Yael Hanein, directrice du Centre de Nanosciences et Nanotechnologies et de l’Institut de Nanomédecine de l’Université de Tel-Aviv, en collaboration avec des chercheurs de l’Université hébraïque de Jérusalem et de l’Institut des Neurosciences de l’Université Newcastle au Royaume Uni a développé une pellicule flexible, sensible à la lumière, susceptible de remplacer une rétine endommagée par la maladie dégénérative de la rétine liée à l’âge (DMLA).
Ces recherches, présentées en mars lors d’une journée d’études deSolve for X, le laboratoire d’idées lancé par Google pour promouvoir les projets “Moonshots”, à mi-chemin entre la science et la science-fiction. Le nouveau dispositif est capable de remplacer l’action des photorécepteurs naturels de l’œil, lorsqu’ils sont détruits par la maladie dégénérative de la rétine liée à l’âge (DMLA), affection due à la dégradation progressive de la macula, partie centrale de la rétine, provoquant la détérioration des capacités visuelles à partir de 50 ans, et le plus souvent après 65 ans.
Les scientifiques ont jusqu’à présent tenté de développer différents implants capables de «voir» la lumière et d’envoyer des signaux visuels au cerveau, pour contrer les effets de la maladie. Mais les dispositifs mis au point jusqu’ici sont peu malléables, utilisent des pièces métalliques susceptibles d’être mal acceptées par l’organisme, et un système de câblage encombrant.
Nanotiges et nanotubes de carbone
Le Prof. Hanein et ses collègues ont mis au point un dispositif plus compact sans sacrifier la qualité de la résolution. Combinant des nanotiges semi-conductrices et des nanotubes de carbone, ils sont parvenus à créer une pellicule autonome, flexible et photosensible qui a le potentiel de fonctionner à la place de la rétine endommagée.
Les tests ont montré que le film absorbe la lumière et stimule l’activité neuronale. Les chercheurs ont conclu que le dispositif est plus durable, plus souple et plus efficace que les technologies développées jusqu’à présent, et provoque une meilleure réponse du système neuronal. Les autres chercheurs de l’équipe sont Lilach Bareket, Moshe David-Pur, le Dr. David Rand, le Dr. Roy Soumyendu, le Prof. Ori Cheshnovsky et les doctorants Gur Lubin, Jacob Ben-Dov, de l’Université de Tel-Aviv; Nir Waiskopf et le Prof. Uri Banin de l’Université hébraïque de Jérusalem; et les Dr. Cyril Eleftheriou et Evelyne Sernagor de l’Université de Newcastle. L’étude a été financée par le ministère israélien de la Science et de la Technologie, le Conseil européen de la recherche et le Conseil pour la recherche en Sciences biologiques et Biotechnologie en Grande-Bretagne.
Publication dans l’American Chemical Society Nano Letters, nov. 2014.
http://phys.org/news/2014-11-
Publication sur le site des Amis français de l’Université de Tel Aviv
Yael Hanein and colleagues point out that a growing range of medical devices has become available to treat conditions, including visual impairment, that involve sending sensory signals to the brain. Patients with one type of eye disorder called age-related macular degeneration (AMD), for example, could potentially benefit from such a device, they say. AMD usually affects people age 60 or older who have damage to a specific part of the retina, limiting their vision.
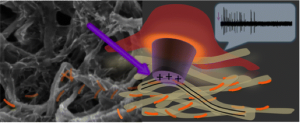
Scientists are trying different approaches to develop an implant that can « see » light and send visual signals to a person’s brain, countering the effects of AMD and related vision disorders. But many attempts so far use metallic parts, cumbersome wiring or have low resolution. The researchers, an interdisciplinary team from Tel Aviv University, the Hebrew University of Jerusalem Centers for Nanoscience and Nanotechnology and Newcastle University, wanted to make a more compact device.
The researchers combined semiconductor nanorods and carbon nanotubes to create a wireless, light-sensitive, flexible film that could potentially act in the place of a damaged retina. When they tested it with a chick retina that normally doesn’t respond to light, they found that the film absorbed light and, in response, sparked neuronal activity. In comparison with other technologies, the researchers conclude theirs is more durable, flexible and efficient, as well as better able to stimulate neurons.
Read more at: http://phys.org/news/2014-11-artificial-retina-vision.html#jCp
http://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/
See also article from Sivan Cohen-Weisenfeld, French friends of Tel Aviv Unviersity [:]