Hémorragies : l'Université d'Ariel (Israël) montre que le gallium empêche les caillots sanguins mortels

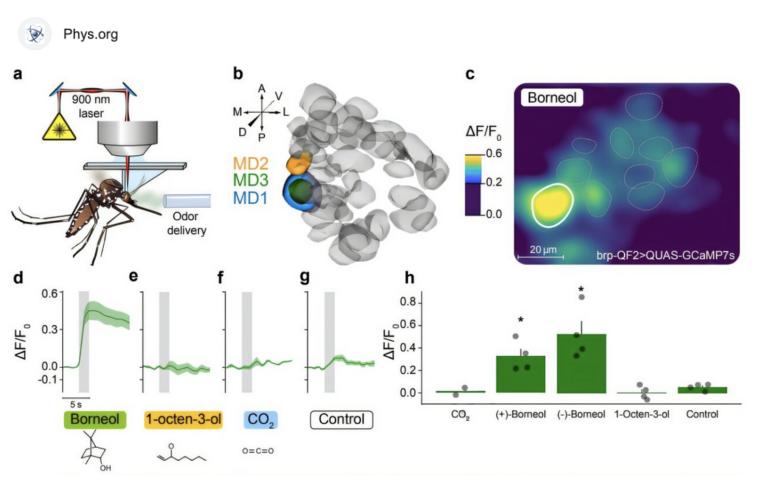
[:fr]Bel exemple de sérendipité. Dans le cadre de recherches sur un autre sujet, le scientifique Moshe Rogosnitzky de l’Université Ariel en Israël, a découvert que le gallium, actuellement utilisé sous forme liquide (nitrate de gallium) pour arrêter la perte osseuse chez les patients atteints de cancer, peut stopper rapidement le saignement des plaies profondes sans causer de caillots de sang.
L’hémorragie reste l’une des principales causes de décès, suite aux attaques à l’arme blanche de terroristes. Moshe Rogosnitzky a découvert une nouvelle méthode qui permet de stopper le saignement incontrôlé des victimes attaquées à coups de couteau par des terroristes, ce qui pourrait sauver d’innombrables vies.
Au cours de la vague de terreur qui frappe Israël, beaucoup de victimes ont perdu trop de sang, ce qui a entraîné leur mort. Jusqu’à présent, les seules solutions existantes face aux blessures profondes à l’arme blanche sont trop faibles ou si fortes qu’elles causent des caillots sanguins mortels. Même les premiers intervenants médicaux les plus compétents ne disposent souvent pas de solutions efficaces pour sauver des vies, alors que chaque seconde compte.
Des recherches approfondies ont montré que le gallium est un très puissant anti-infectieux et qu’il accélère la guérison des blessures causées par des entailles profondes, souvent produites par les couteaux et d’autres types d’armes utilisées par les terroristes.
Le gallium fonctionne par induction de « floculation » de la protéine de coagulation du sang (fibrinogène). Cela se traduit par la formation de caillot externe. Contrairement aux autres traitements des blessures hémorragiques, le gallium ne provoque pas de mécanismes de coagulation dans le sang. Cela évite le risque élevé de caillots sanguins mortels internes.
Selon Moshe Rogosnitzky, le gallium peut « augmenter considérablement les chances de survie des victimes. Mais il faut faire passer cette découverte du laboratoire à la recherche clinique le plus rapidement possible. Plus vite il arrivera sur le marché, plus vite il pourra être utilisé pour sauver des vies ».
Traduit et adapté par Esther Amar pour Israël Science Info[:en]An Ariel University researcher has discovered a new method to stop uncontrolled bleeding of victims of stab wounds which could save countless lives from terrorist attacks.
During the wave of terror currently engulfing Israel in which dozens have been murdered and scores more wounded, including mothers, children and the elderly, many of those innocently targeted have bled to death. Until now the only blood stopping solutions for the type of deep wounds caused by such violent stabbings sustained by the injured, are either too weak or so strong that they cause deadly blood clots. Even the most able medical first responders often do not have the most effective solutions to save lives when every second counts.
Israeli scientist Moshe Rogosnitzky has serendipitously discovered that gallium, a biometal currently used to stop bone loss in cancer patients, in liquid form (known as gallium nitrate), can rapidly halt bleeding from deep wounds without causing blood clots.
The use of gallium for stopping bleeding from deep cuts provides additional benefits. Extensive research has shown that gallium is a very powerful anti-infective and speeds the healing of injuries caused by deep gashes which are often produced by the knives and other type of weapons used by terrorists.
Gallium works by inducing “flocculation” of the clotting protein in blood known as fibrinogen. This results in external clot formation. In stark contrast to other treatments for bleeding wounds, gallium does not induce clotting mechanisms in the blood. This avoids the highest risk of existing technologies that run the risk of causing deadly internal blood clots.
According to Rogosnitzky, Gallium has the potential to “dramatically increase the chances of survival by victims of terror or accidents. However, it is vital to get this discovery from the lab to the clinic as quickly as possible. The sooner it gets to the market, the sooner it can be used effectively to save lives.”
At this stage, gallium has to undergo studies to determine the optimal dose and delivery method prior to filing for marketing authorization by the health authorities. In addition, a comparative efficacy trial with other technologies for stopping bleeding needs to occur.
In order to speed up the process for clinical development and availability of gallium, Stop the Bleeding, an online fundraising campaign has been initiated through We Fund the Cure – a US-based nonprofit. The researchers urgently need funding to move forward to the next stage.
“Unfortunately, there seems to be no immediate end in sight to the kind of violent attacks facing Israelis. Gallium can provide instantaneous help to victims in Israel. Our goal is to place gallium in every first aid kit and every ambulance, ensuring that every stabbing victim has an increased chance of survival. In order to move forward quickly we need resources for clinical testing.” said Rogosnitzky. “Moreover,” he added, “as blood loss remains the leading cause of death from stabbings and other external injuries, it is our hope that this innovation can help innocent victims of violent crime or accidents throughout the world by significantly reducing mortality rate and providing an effective and safe answer for blood loss from wounds.”[:]