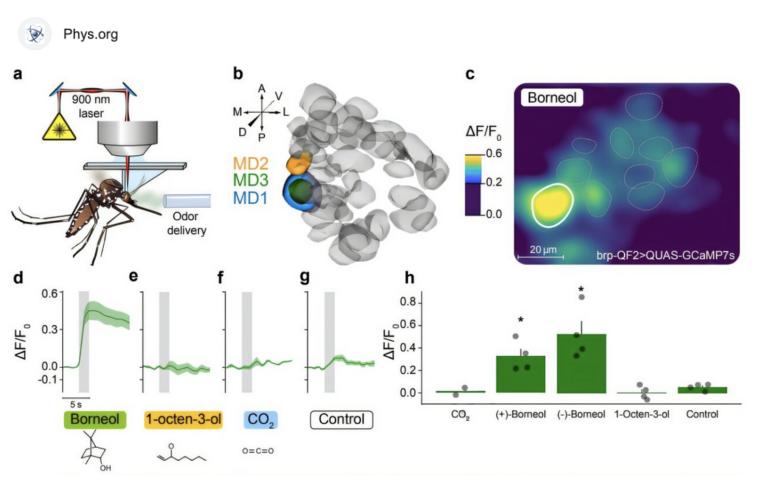
Cancer cutané (mélanome), l'Université Hébraïque de Jérusalem recommande de protéger dès la prime enfance

[:fr]Le mélanome est le cancer le plus rare mais c’est également le plus dangereux des cancers cutanés. En 2010, en France il a entrainé le décès de 1570 personnes. La responsabilité du rayonnement solaire, et notamment des coups de soleil reçus pendant l’enfance est connue. Une étude israélienne conduite par le Dr Hagai Levine et le Pr Jeremy Kark de l’Université Hébraïque de Jérusalem vient de confirmer que c’est avant l’âge de 10 ans qu’il faut être le plus vigilant. Israël étant un pays d’immigration et profitant d’un niveau d’ensoleillement nettement supérieur à celui de l’Europe, l’étude a comparé le risque de mélanome selon l’âge d’arrivée dans le pays. Le risque est doublé pour les personnes ayant immigré avant l’âge de 10 ans par rapport à celles ayant immigré quelques années plus tard.
Publication dans the International Journal of Cancer, février 2013[:en]A new study conducted using extensive medical records of over one million Israeli adolescents before military service shows clearly how exposure to the Israeli sun of young, light-skinned children increases substantially the risk of cutaneous melanoma (a serious form of skin cancer).
The incidence of cutaneous melanoma is on the rise in all parts of the world where light-skinned people live. Rates have tripled over the last decades in the United States, and the rise was even steeper in Europe.
What about in Israel? What segments of the population are more at risk and at what stage? Dr. Hagai Levine and Prof. Jeremy Kark from the Hebrew University-Hadassah Braun School of Public Health and Community Medicine and other researchers set out to find the answers, using records of young Jewish males who were examined between 1967 and 2005. These men were followed up by data linkage for cancer incidence until the end of 2006. Females were not included because their baseline data were available only for a more recent period.
In their study, the researchers found – not surprisingly – a quadrupled higher risk of skin cancer among native-born Israelis of European origin (including the Americas, Australia and South Africa) and those immigrating from those countries over those of North African or Asian origin.
Israel’s subtropical latitude means residents are exposed to more solar radiation than in much of Europe, and therefore the findings implicate childhood sun exposure as a clear, preventable risk factor for melanoma. But even for those who spent their childhood in Europe, the data showed that those who came to Israel before age 10 had almost double the risk of cutaneous melanoma compared to those who arrived from Europe later in childhood.
The study of melanoma susceptibility according to countries of origin is especially suited to Israel because of the massive immigration that has taken place since the establishment of the state, bringing Jews of varying skin hues from Europe, North Africa and Western Asia.
The study on Israel and cutaneous melanoma was published recently in the International Journal of Cancer. In addition to Dr. Levine and Prof. Kark, researchers from the Israel Defense Forces Medical Corps, the National Cancer Registry and other institutions participated in the work.
They used an extensive database culled from military medical examinations, enabling them to conduct a large-scale migrant cohort study in order to identify high-risk populations and critical periods of sun exposure during childhood, which would aid in directing public health and research efforts.
Israel is one of the few western countries where military service is mandatory. All Israeli Jewish adolescents are obligated to present themselves at age 17 for a medical board examination before military service (even if exempted later from service). Consequently, use of these data provides a generally representative sample of the young Jewish population, particularly of males.
These findings, say the researchers, provide solid support for the importance of stressing the issue of childhood sun exposure, particularly in light skinned people, as a preventable risk factor for cutaneous melanoma and can aid in directing public health and research efforts.
[:]